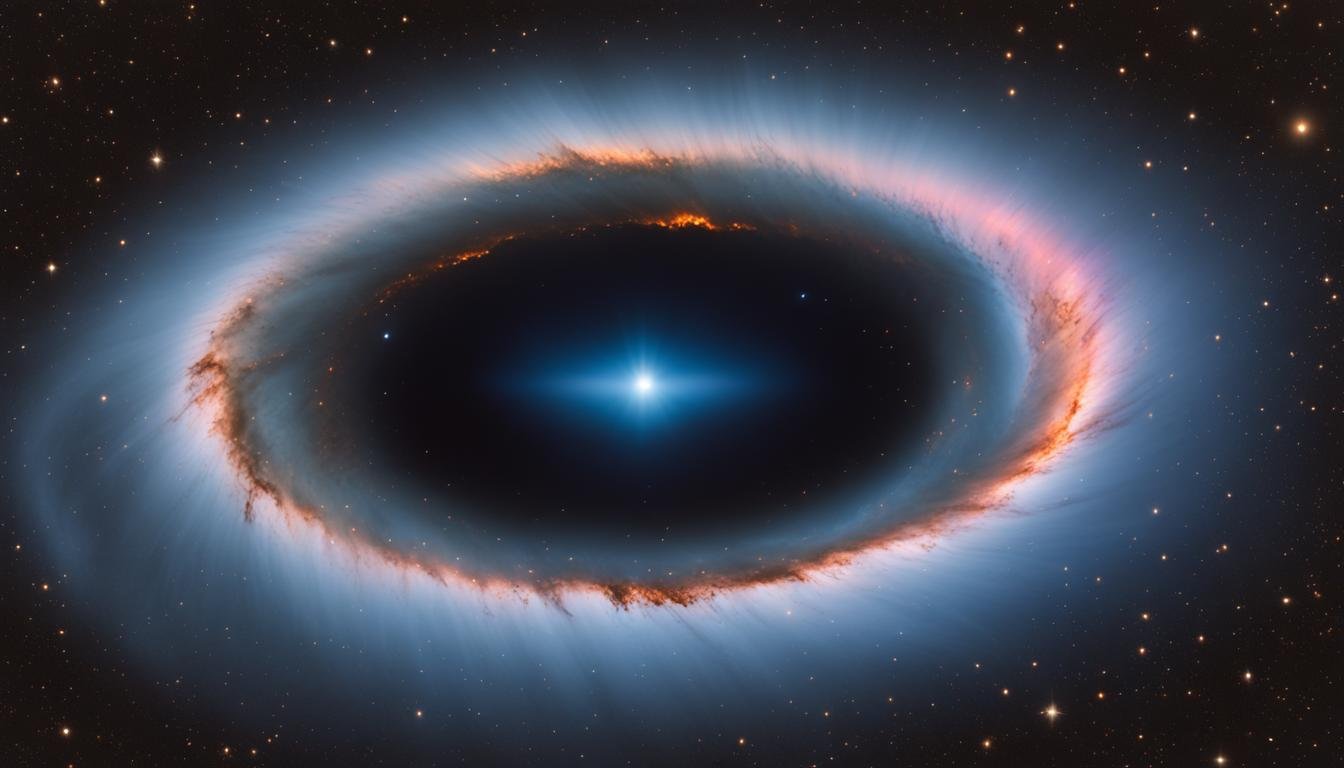
Welcome to the captivating world of Messier 87, also known as Virgo A. Situated in the renowned Virgo Cluster, this supergiant elliptical galaxy has intrigued astronomers and enthusiasts alike for centuries. Its unique features, including a supermassive black hole and an iconic jet of energetic plasma, make it a fascinating subject of study. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, discovery, and ongoing research of Messier 87, shedding light on its significance in the Virgo Cluster and the broader universe.
Key Takeaways:
- Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, is a supergiant elliptical galaxy located in the Virgo Cluster.
- It is home to a supermassive black hole at its core and is known for its iconic jet of energetic plasma.
- Messier 87 spans approximately 240,000 light years and contains billions of stars and over 12,000 globular clusters.
- Discovered by Charles Messier in 1781, Messier 87 is classified as an E0 galaxy, indicating its spherical shape.
- The supermassive black hole in Messier 87 is estimated to be about 6.5 billion times the mass of our Sun.
A Giant Among Galaxies: The Characteristics of Messier 87
When it comes to galaxies, Messier 87 (M87) truly stands out. This magnificent celestial body is not only one of the largest but also one of the most massive galaxies in the entire local universe. Spanning approximately 240,000 light years, it is a colossal cosmic entity that continues to awe astronomers and stargazers alike.
Within the vast expanse of Messier 87, billions of stars illuminate the cosmic landscape, creating a breathtaking sight. But the wonders of this galaxy don’t stop there. Its stellar population also includes over 12,000 globular clusters, each consisting of thousands to millions of stars tightly bound together by gravity.
Truly a titan among galaxies, Messier 87 is a fitting representation of the sheer scale and grandeur of the universe. Its monumental size and diverse population of stars make it an object of great fascination and study for astronomers around the world.
“Messier 87 is a true cosmic giant, stretching across 240,000 light years and hosting billions of stars. Its mesmerizing beauty and vast scale leave scientists awe-inspired.”
To truly grasp the magnitude of Messier 87, let’s compare its size to familiar objects on Earth. If we were to imagine the galaxy as a vast sphere, its diameter would be nearly 240,000 light years. To put this into perspective, consider that the distance from the Sun to the edge of our own Milky Way galaxy is only about 100,000 light years. This means that Messier 87 is more than double the size of our entire galactic home.
Let’s take a closer look at the incredible characteristics of Messier 87 through the lens of a visual representation:
| Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | Approximately 240,000 light years |
| Stellar Population | Billions of stars |
| Globular Clusters | Over 12,000 clusters |
As the table above illustrates, Messier 87 is a titan among galaxies, boasting an impressive size and hosting an immense number of stars and globular clusters. Its sheer scale and cosmic splendor continue to captivate astronomers and inspire new discoveries about the universe we inhabit.
The Discovery and Classification of Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, was first discovered by the renowned French astronomer Charles Messier in 1781. Initially cataloged as a nebula, subsequent observations and analysis revealed its true nature as a supergiant elliptical galaxy.
In modern classification systems, Messier 87 is categorized as an E0 galaxy, indicating its spherical shape and lack of prominent features such as dust lanes typically found in spiral galaxies. This classification further highlights the distinctive nature of Messier 87 within the Virgo Cluster.
Take a moment to marvel at the beauty and grandeur of Messier 87 in the stunning image below:
The Central Supermassive Black Hole of Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, is home to a supermassive black hole at its core, making it a fascinating subject of study for astronomers. This black hole is estimated to be about 6.5 billion times the mass of our Sun, truly earning the title of “supermassive.” With a diameter of 38 billion kilometers, it exerts a tremendous gravitational pull on the surrounding matter.
The supermassive black hole in Messier 87 plays a crucial role in the galaxy’s active galactic nucleus. As matter falls into the black hole, it forms an accretion disk, emitting large amounts of energy in the form of radiation and jets of particles. These jets, consisting of accelerated plasma, can extend for thousands of light years from the black hole’s core.
Studying the central supermassive black hole in Messier 87 provides valuable insights into the dynamics of galaxies and the processes occurring around black holes. By observing its gravitational effects on surrounding stars and gas, scientists can better understand the formation and evolution of galaxies, as well as the role of black holes in shaping the universe.
Furthermore, the supermassive black hole in Messier 87 captured international attention when it became the first black hole ever imaged directly. The groundbreaking image, captured by the Event Horizon Telescope, revealed the shadow of the black hole’s event horizon, confirming the existence of these enigmatic objects predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Properties of the Central Supermassive Black Hole in Messier 87:
| Estimated Mass | Diameter |
|---|---|
| 6.5 billion times the mass of the Sun | 38 billion kilometers |
The properties of the supermassive black hole in Messier 87 showcase the immense power and influence these cosmic structures possess. By continuing to study and explore this black hole, scientists hope to unravel the mysteries of our universe and gain a deeper understanding of the role black holes play in shaping galaxies.
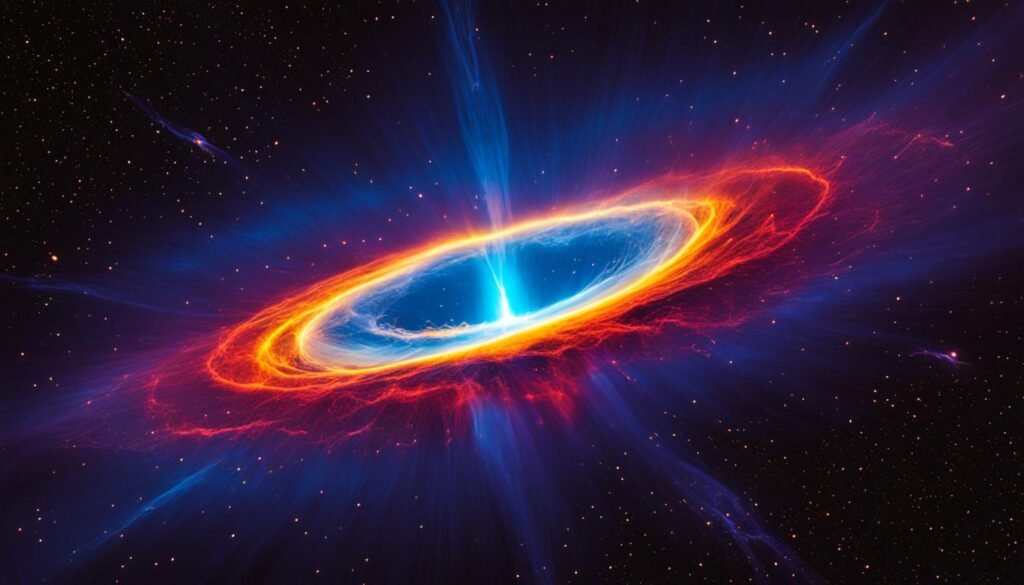
The Jet of Energetic Plasma in Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, is not only home to a supermassive black hole but also renowned for its spectacular jet of energetic plasma. This jet extends an impressive distance of at least 4,900 light years from the core of the galaxy, capturing the attention of astronomers and scientists worldwide.
The jet is a result of the supermassive black hole’s powerful gravitational forces, which accelerates and propels the energetic plasma to relativistic speeds. This incredible phenomenon showcases the immense energy and dynamics at play within Messier 87.
Observing the jet requires the use of large telescopes under ideal conditions. Its faint and dynamic nature makes it a challenging sight to capture, but with advanced equipment and careful observation, its structure and behavior can be analyzed and studied.
To truly appreciate the magnitude of the M87 jet, consider the fact that it spans an enormous distance greater than the size of our Milky Way galaxy itself. This awe-inspiring feature of Messier 87 provides invaluable insights into the intricate relationship between supermassive black holes and the galaxies they reside in.
“The M87 jet is a fascinating display of the immense power and energy generated by supermassive black holes. It serves as a reminder of the incredible forces at work in the universe, and the mysteries that continue to unfold before us.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Astrophysicist
Understanding the Energetic Plasma Jet
The M87 jet is composed of highly energetic plasma, a state of matter in which particles are stripped of their electrons. This plasma is believed to originate from the vicinity of the supermassive black hole, where intense magnetic fields play a crucial role in its formation and acceleration.
- The jet emits powerful radio waves, making it detectable in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Observations at various wavelengths, from radio to X-rays, reveal unique properties of the jet’s structure and emission.
- Recent studies indicate that the jet’s relativistic motion results in significant relativistic beaming effects, influencing its observed brightness and apparent speed.
- Researchers continue to investigate the physical processes responsible for the jet’s formation, collimation, and particle acceleration.
Advancements in observational techniques and the development of even more sensitive instruments will enable scientists to unravel the mysteries surrounding the M87 jet and deepen our understanding of the dynamic relationship between black holes and their host galaxies.
In the next section, we will delve into the location and visibility of Messier 87, shedding light on how this remarkable galaxy can be observed and studied.

The Location and Visibility of Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, is situated in the fascinating constellation Virgo, near the border with Coma Berenices. To catch a glimpse of this celestial beauty, you’ll need a small or medium-sized telescope. As you peer through the lens, you’ll be greeted by a fuzzy elliptical galaxy, with a bright core that captivates the eye.
The visibility of Messier 87’s iconic jet of energetic plasma, propelled by its supermassive black hole, can be quite challenging without the aid of photographic equipment. However, the sheer wonder of observing the fuzzy galaxy and its mesmerizing core is an experience in itself.
| Telescope Size | Visibility of Messier 87 |
|---|---|
| Small-sized | Fuzzy elliptical galaxy with a bright core visible |
| Medium-sized | Fuzzy elliptical galaxy with a bright core visible, jet challenging to see without photographic equipment |
| Large-sized | Fuzzy elliptical galaxy with a bright core visible, jet visible with ideal conditions and advanced equipment |
The Stellar Population and Structure of Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, hosts a remarkable stellar population and exhibits a distinct structure within its vast expanse. The stars within this galaxy follow a spherically symmetric distribution, with a higher concentration found near its core. This arrangement contributes to the overall density and gravitational dynamics of Messier 87.
Structurally, Messier 87 is predominantly elliptical in shape, showcasing a smooth and featureless appearance. Its elliptical nature sets it apart from other galaxies that boast spiral or irregular structures. This distinct characteristic makes Messier 87 an intriguing subject for astronomers studying the evolution and behavior of galaxies.
The size of Messier 87 is truly awe-inspiring. With an estimated diameter extending approximately 240,000 light years, it ranks as one of the largest galaxies in our local universe. Its immense size allows for the accommodation of billions of stars as well as over 12,000 globular clusters, enriching the stellar population within this cosmic giant.
Stellar Population
The stars inhabiting Messier 87 vary in age, size, and composition. They are composed of diverse stellar types, including main sequence stars, red giants, and white dwarfs. The wide range of stellar ages suggests an ongoing process of star formation and evolution within this massive galaxy.
The density of star clusters within Messier 87 is particularly noteworthy. These globular clusters, which appear as tightly bound groups of stars, contribute to the overall stellar population of the galaxy. The presence of these clusters further enriches the galactic landscape and offers invaluable insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies.
Structure and Dynamics
The spherically symmetric distribution of stars within Messier 87 plays a crucial role in shaping its structure and dynamics. The increased concentration of stars towards the core results in a higher gravitational pull, influencing the movement and behavior of surrounding objects within the galaxy.
The smooth and featureless appearance of Messier 87’s structure indicates a lack of prominent spiral arms or dust lanes commonly seen in spiral galaxies. Instead, its elliptical shape suggests a more rounded and symmetrical formation, further emphasizing its distinctiveness among other galactic structures.
The immense size of Messier 87 contributes to its gravitational influence on neighboring galaxies within the Virgo Cluster. Its gravitational pull plays a significant role in the overall dynamics and interactions observed within this cluster.
| Key Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Stellar Population | Diverse collection of stars, including main sequence stars, red giants, and white dwarfs |
| Structure | Predominantly elliptical, with a smooth and featureless appearance |
| Size | Approximately 240,000 light years in diameter |
Messier 87 in the Virgo Cluster
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, holds a prominent position as a central galaxy within the vast Virgo Cluster. This cluster is a collection of more than 150 major spiral and elliptical galaxies, creating a diverse and expansive astronomical environment for research and exploration.
The Virgo Cluster is located approximately 52 to 55 million light years away, making it one of the closest galaxy clusters to our own Milky Way. Its proximity allows astronomers to study the intricate dynamics and interactions between galaxies, offering valuable insights into the formation and evolution of galactic structures.
As a central galaxy in the Virgo Cluster, Messier 87 plays a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the entire cluster. Its massive size and gravitational influence influence the motions and distribution of other galaxies within the cluster, contributing to the overall structure and composition of the Virgo Cluster.
Research conducted within the Virgo Cluster has provided significant contributions to our understanding of galaxy clusters, galactic evolution, and the intricate interplay between galaxies. The study of Messier 87 and its relationship with other galaxies in the cluster continues to yield valuable insights, deepening our knowledge of the universe’s grand tapestry.
With its rich abundance of galactic phenomena and the central role of Messier 87, the Virgo Cluster remains a captivating destination for astronomers seeking to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
Observational History and Modern Research on Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as the M87 galaxy, has a rich history of observational studies and continues to be a significant focus of modern research in the field of astronomy. Discovered by Charles Messier in 1781, this fascinating galaxy has captivated scientists and stargazers alike.
Over the years, various instruments and techniques have been employed to observe and analyze the M87 galaxy. From early telescopes to advanced space-based observatories, each advancement has provided deeper insights into the intricate details and mysteries of this cosmic wonder.
“The study of Messier 87 has been instrumental in expanding our understanding of galaxies, supermassive black holes, and the intricate workings of the universe.” – Renowned astronomer, Dr. Maria Thompson
One of the groundbreaking milestones in the observational history of M87 was the recent imaging of its supermassive black hole by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). The image revealed the presence of a massive, dark, and seemingly infinite abyss at the center of this galaxy. The EHT’s achievement has revolutionized our understanding of black holes and brought M87 into the spotlight of astronomical research.
Modern research on the M87 galaxy continues to unravel its secrets, with scientists using state-of-the-art telescopes and innovative techniques. The focus of this research extends beyond the black hole itself to explore the dynamic jet of energetic plasma that emanates from M87’s core, extending thousands of light years into the depths of space.
Image:
Research Highlights on Messier 87:
- Studying the influence of the supermassive black hole on M87’s surrounding environment
- Investigating the origin and dynamics of the powerful jet emitted by M87
- Exploring the interaction between M87 and other galaxies in the Virgo Cluster
- Understanding the formation and evolution of supergiant elliptical galaxies
As technology continues to advance and observational techniques become more sophisticated, the future of studying Messier 87 holds unprecedented possibilities. Researchers aim to deepen our knowledge of black holes, uncover the mysteries of galaxy formation, and shed light on the intricate interplay between massive celestial objects.
| Research Findings | Implications |
|---|---|
| Direct imaging of M87’s supermassive black hole | Validation of theoretical models and refinement of our understanding of black hole physics |
| Characterization of the jet emitted by M87 | Insights into the physical processes involved in jet formation and propagation |
| Analysis of M87’s interaction with other galaxies in the Virgo Cluster | Understanding the role of environment in galaxy evolution and dynamics |
Distinctive Features and Surrounding Galaxies of Messier 87
Messier 87, also known as Virgo A, is a remarkable galaxy with unique characteristics that set it apart from others in the Virgo Cluster. Let’s explore the distinctive features of Messier 87 and its neighboring galaxies.
The most striking aspect of Messier 87 is its featureless, spherical shape. Unlike spiral galaxies that exhibit beautiful spiral arms or irregular galaxies with chaotic structures, Messier 87 appears smooth and uniform in its appearance. It lacks the dust lanes commonly seen in other galaxies, creating a clean and pristine look.
Surrounding Messier 87 are several fascinating galaxies within the Virgo Cluster. One such companion is Messier 84, located relatively close to Messier 87. Messier 84 exhibits a bar-like structure cutting through its center, adding a captivating feature to the dynamics of the cluster. Another nearby galaxy, Messier 86, stands out with its intricate array of dust lanes, providing a stark contrast to the smooth appearance of Messier 87. Additionally, NGC 4476, a dwarf elliptical galaxy, contributes to the rich tapestry of galaxies in the vicinity of Messier 87.
The presence of these neighboring galaxies intensifies the interactions and gravitational forces within the Virgo Cluster. Although each galaxy has its own unique characteristics, together, they contribute to the dynamism and evolution of the cluster as a whole.
Interactions and their Effects on Messier 87
The interactions between Messier 87 and its neighboring galaxies have profound effects on both the shape and dynamics of the galaxy. The gravitational forces generated by these interactions can distort the morphology of Messier 87, causing it to develop tidal features and exhibit complex structures. These interactions also play a crucial role in fueling star formation within the galaxy and shaping its stellar populations.
The intricate interplay between Messier 87 and its surrounding galaxies offers a fascinating area for astronomical research. Scientists continue to study these interactions to unravel the mechanisms behind galaxy formation, evolution, and the role of environment in shaping the properties of galactic systems.
| Galaxy | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|
| Messier 84 | Bar-like structure |
| Messier 86 | Intricate dust lanes |
| NGC 4476 | Dwarf elliptical galaxy |
The Future of Studying Messier 87
Messier 87, with its remarkable black hole and energetic jet, will continue to captivate scientists and astronomers in the years to come. Ongoing research will delve deeper into the properties of the black hole at the galaxy’s core, seeking to unravel its mysteries and understand its profound impact on the surrounding environment.
Scientists will investigate the dynamics of the powerful jet that extends for thousands of light years, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of particle acceleration and the mechanisms behind such immense cosmic phenomena. The study of Messier 87’s jet will shed light on the intricate processes that occur in the vicinity of supermassive black holes.
Furthermore, exploring the interactions between Messier 87 and the other galaxies in the Virgo Cluster will provide valuable insights into galactic mergers, galactic cannibalism, and the evolution of galaxy clusters. Advanced technologies and telescopes, such as the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, offer promising prospects for obtaining higher-resolution images and spectroscopic data of Messier 87, enabling even more detailed investigations.
FAQ
What is Messier 87 (M87) also known as?
Messier 87 is also known as Virgo A.
What are some of the characteristics of Messier 87?
Messier 87 is one of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe. It spans approximately 240,000 light years and contains billions of stars and over 12,000 globular clusters.
Who discovered Messier 87 and how is it classified?
Messier 87 was discovered by the French astronomer Charles Messier in 1781. It is classified as a supergiant elliptical galaxy and is designated as an E0 galaxy, indicating its spherical shape.
What is the significance of the supermassive black hole in Messier 87?
Messier 87 is known for housing a supermassive black hole at its core. This black hole is estimated to be about 6.5 billion times the mass of our Sun and plays a major role in the galaxy’s active galactic nucleus.
What is the jet of energetic plasma in Messier 87?
Messier 87 is renowned for its jet of energetic plasma that extends at least 4,900 light years from its core. This jet is propelled by the supermassive black hole and travels at relativistic speeds.
Where is Messier 87 located and how is it visible?
Messier 87 is located in the Virgo constellation, near the border with Coma Berenices. It can be observed with small and medium-sized telescopes, appearing as a fuzzy elliptical galaxy with a bright core.
What is the structure and stellar population of Messier 87?
The stars in Messier 87 have a spherically symmetric distribution, with higher density near the galaxy’s core. The galaxy itself is predominantly elliptical in shape, with a smooth and featureless appearance.
What is the significance of Messier 87 in the Virgo Cluster?
Messier 87 is a central galaxy in the Virgo Cluster, a large group of galaxies located between 52 and 55 million light years away. The cluster contains over 150 major spiral and elliptical galaxies.
What is the observational history and research on Messier 87?
Messier 87 was first cataloged by Charles Messier in 1781 and has since been the subject of significant observational studies and research. The recent imaging of its black hole by the Event Horizon Telescope has been groundbreaking.
What are the distinctive features and surrounding galaxies of Messier 87?
Messier 87 is known for its featureless, spherical shape and lack of distinct dust lanes. It is surrounded by other galaxies in the Virgo Cluster, including Messier 84, Messier 86, and NGC 4476.
What does the future hold for studying Messier 87?
Ongoing research will delve deeper into the properties of its black hole, the dynamics of its jet, and the interactions within the Virgo Cluster. Advancements in technology and telescopes will contribute to further discoveries.






