| Genitive | Camelopardalis |
| Abbreviation | Cam |
| Pronunciation | (kəˌmɛloʊˈpɑːrdəlɪs) |
| Main Stars | 2, 8 |
| Brightest Star | β Cam (4.03m) |
| Right Ascension | 3 hours to 14 hours |
| Declination | 86 deg to -52 deg |
| Sq. Deg. Area | 757 |
| Crosses Meridian | 9PM, Feb |
| Visible Lat. Range | +90, -10 deg (°) |
| Best Viewing Season | Winter (Northern Hemisphere) |
As you gaze upwards, the night sky presents an intricate tapestry of celestial wonder, punctuated by the subtle yet fascinating Constellation Camelopardalis. Occupying an impressive 757 square degrees, this northern celestial marvel bears a storied history dating back to its 17th-century delineation by Petrus Plancius. Connoisseurs of the cosmos, such as yourself, will appreciate the Camelopardalis Star Pattern, with its significant contributions to the field of astronomy. Encapsulating prodigious deep space phenomena, Camelopardalis Constellation Stars like the bright Beta Camelopardalis reveal a universe beyond our own. In your quest for astronomical enlightenment, the Camelopardalis Constellation History stands as a testament to human curiosity and exploration, while current Camelopardalis Constellation Information continues to ignite the passion of stargazers worldwide.
Dive into the splendor of the giraffe-shaped constellation and you’ll unearth a plethora of celestial gems – from the whimsical dance of meteor showers to the incessant glimmer of distant galaxies – each beckoning you to discover more. Now, let us embark on a stellar journey, unlocking the secrets of this lesser-known but equally compelling constellation.
Key Takeaways
- Camelopardalis stands out in the night sky covering a vast area and offering a myriad of stars and deep space phenomena to discover.
- The constellation’s brightest star, Beta Camelopardalis, is a binary system that illuminates the surrounding celestial canvas.
- Kemble’s Cascade within Camelopardalis offers an enchanting asterism, leading observers to the open cluster NGC 1502.
- Camelopardalis boasts significant astronomical attractions like the Oyster Nebula (NGC 1501), adding to its uniqueness.
- While devoid of any Messier objects, the constellation’s history and current observations continue to captivate astronomy enthusiasts.
- The October Camelopardalids meteor shower is a notable event for skywatchers, highlighting the constellation’s dynamic nature.
Unlocking the Secrets of Constellation Camelopardalis
As you delve into the depths of the night sky, the Camelopardalis constellation holds within its expanse a rich tapestry of celestial stories and stellar wonders. With no root in ancient mythology, as it came to be recognized in the era of telescopic astronomy, Camelopardalis offers a unique glimpse into the cosmos that continues to fascinate astronomers and stargazers alike.
Origin of the Name and Historical Discoveries
Constellation Camelopardalis, often overlooked due to its faint constellations, bears an origin story that reflects humanity’s relentless pursuit of knowledge. Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius was the principal creator of this constellation, with Jakob Bartsch later immortalizing it in his respected 1624 star map. Perhaps drawing inspiration from the Book of Genesis, Bartsch illustrated Camelopardalis as a camel, a choice that seems at odds with the commonly accepted giraffe depiction. These contradictory inspirations behind the Camelopardalis Constellation Facts only add to its enigmatic allure.
Star Patterns and the Giraffe in the Sky
With stars scattered across the sky like faint spots on a giraffe’s coat, the patterns of Camelopardalis are subtle yet significant. This constellation, meandering loosely across the celestial realm, invites you to trace the outlines of what is poetically envisioned as the sky’s gentle giant.
Notable Features: Kemble’s Cascade and Star Clusters
Among the mosaic of starry configurations, Kemble’s Cascade stands out as a signature asterism. Named by the renowned astronomy columnist Walter Scott Houston, this linear arrangement of stars seems to cascade down toward the open star cluster NGC 1502. At the cascade’s terminus lies the exceptional Camelopardalis Star Cluster, a stunning collection of stars that anchors this asterism’s flow in the vastness of space.
| Feature | Description | Notability |
|---|---|---|
| Kemble’s Cascade | Asterism resembling a string of pearls | A cosmic waterfall culminating in NGC 1502 |
| NGC 1502 | Open star cluster | End point of Kemble’s Cascade and home to numerous hot, young stars |
Embracing these celestial features, your journey through the constellation Camelopardalis becomes an exploration of cosmic mysteries and a testament to the wonders the universe holds—both known and yet to be discovered.
Camelopardalis Constellation Stars
As you gaze upon the vast canvas of the night sky, the Camelopardalis constellation may not immediately catch your eye, yet it offers rich astronomical treasures for those willing to explore. Beyond its historical significance, the constellation’s star pattern serves as a map to a multitude of celestial wonders within its boundaries.
Guiding You to Beta Camelopardalis: The Brightest Star
When probing the Camelopardalis constellation, your journey begins with Beta Camelopardalis. Shining the brightest among the Camelopardalis constellation stars, this binary system features a resplendent G-type supergiant. Approximately 1,000 light years from Earth, its warm glow reaches us with an apparent magnitude of 4.03, serving as a beacon in the celestial architecture of the night sky.

The Varied Luminaries of Camelopardalis: Binary and Variable Stars
In this unique swath of sky, you’ll encounter a symphony of luminous entities, from binaries to variable stars. Among them, CS Camelopardalis stands out, a star that exemplifies the characteristics of an Alpha Cygni variable and is accompanied by a distant celestial partner 3,000 light years away with a magnitude of 8.7.
Survey of the Lesser-Known Stars in the Constellation
While the luminaries like Beta and CS Camelopardalis capture most of the attention, there are myriad lesser-known stars awaiting your discovery. Sigma 1694 Camelopardalis, often symbolized as the giraffe’s head, and VZ Camelopardalis, a semi-regular variable star that glows red against the cosmic backdrop, enhance the Camelopardalis star pattern. Uncover these and more as you delve into the Camelopardalis constellation discoveries, each star contributing its own chapter to the tale of our galaxy.
Navigating the Night Sky: Locating the Camelopardalis Star Cluster
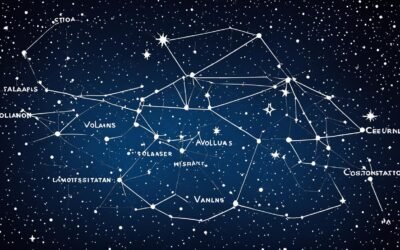
Your quest to uncover the mysteries of the stars begins with the immaculate sky maps provided by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and Sky & Telescope magazine. With the guidance of the detailed Camelopardalis Constellation Map, you can embark on a celestial journey to uncover this elusive constellation. Tucked away near the northern celestial pole, Camelopardalis’ vast expanse is revealed through the constellation map’s precise depiction.
Whether you are a seasoned astronomer or a curious stargazer, armed with this map, your exploration of the night sky is transformed into an engaging and attainable adventure.
Space Mapping: The IAU and Sky & Telescope’s Constellation Map
The constellation spans a grand 61 degrees of the sky and is predominantly visible from the Northern Hemisphere. Its celestial coordinates allow for accurate tracking, presenting an opportunity to witness the connectivity between ancient lore and modern astronomy. The Camelopardalis Constellation Information provided by these authoritative sources is integral for appreciating the constellation’s splendor from any vantage point.
Stellar Coordinates: Using Azimuth and Altitude to Your Advantage
Utilize your newfound knowledge of azimuth and altitude to pinpoint Camelopardalis’ position. At 20:39 UTC, it reaches an altitude of 74.4°, with an azimuth of 38.7°, making it an ideal target for your celestial observations. Leverage these coordinates alongside the Camelopardalis Constellation Map and immerse yourself in the enchantment of the night sky, where each star tells a story, and every constellation has its secrets awaiting your discovery.
Deep Sky Wonders within Camelopardalis
If you’re a stargazer with a penchant for peering into the depths of space, the Camelopardalis constellation holds an array of cosmic treasures. Known for its elusive yet fulgent deep sky objects, Camelopardalis offers more than just a smattering of stars; it is home to celestial discoveries that leave even seasoned astronomers in awe. This celestial expanse is brimming with intriguing deep sky objects Camelopardalis, forging a path of discovery across the universe.
Exploring Galaxies Far Beyond: NGC 2403 and IC 342
Embark on an interstellar journey to the outer reaches of the known galaxy with Camelopardalis Constellation Discoveries, showcasing marvels like NGC 2403, a spiral galaxy that sits 8 million light years from Earth. Revealing a symphony of star formation, its well-defined spiral arms twist through the cosmos, capturing the imagination. Similarly, the more enigmatic IC 342 waits to be unravelled, lying approximately 10.7 million light years away, veiled by galactic dust that challenges its observance, yet entices with the potential for revelation.
The Oyster Nebula: A Celestial Gem
Within the celestial tapestry of Camelopardalis, the Oyster Nebula, formally known as NGC 1501, emerges as a luminous planetary nebula. This celestial pearl emits an ethereal glow that typifies nebular splendor. Its radiant visage is the result of an expired star shedding its outer layers, providing an otherworldly spectacle for onlookers.
Dwarf Galaxies and Their Super Star Clusters
Contrasting with the high-energy dynamics of larger galaxies, the dwarf galaxy NGC 1569 conceals within its confines two super star clusters. These clusters are stellar nurseries, brimming with young, hot stars that illuminate the volatile processes of star creation. Witness the ballet of creation and destruction that plays out over millions of years in this compact galactic domain.
The Story Behind Camelopardalis Constellation History
When you gaze up at the vast canvas of the night sky, the Camelopardalis Constellation might not be the first to catch your eye. Yet, its subtle configuration belies a rich tapestry **Camelopardalis Constellation History** unwinds. Distinguished from the well-known constellations rooted in ancient mythology, the stars of Camelopardalis tell a tale dating back to the Renaissance era’s fervor for exploration and discovery.
In the 17th century, the Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius placed Camelopardalis amongst the celestial bodies, inspired by the giraffe—an enigmatic entity representing the wonders of distant lands encountered by European explorers. The very term *Camelopardalis* evokes images of this long-necked creature, infusing the constellation’s identity with a sense of the exotic and the unknown. Although lacking the brightness of its neighbors, the **Camelopardalis Constellation Stars** have made a modest yet indelible mark upon our understanding of the cosmos.
You’ll find Camelopardalis positioned as the 18th largest constellation, offering an assembly of luminous points that, while primarily faint, includes 174 stars brighter than magnitude 6.5. Below, witness a detailed tabulation, mapping the principal stars that form this giraffe of the galaxy, each contributing to the cluster’s low-key yet captivating portrait in the night sky.
| Star Name | Apparent Magnitude | Distance (Light Years) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta Camelopardalis | 4.03 | 1,000 | A binary system with a giant primary component |
| CS Camelopardalis | 4.21 | 3,000 | Noted for its variability and companion star |
| Alpha Camelopardalis | 4.29 | 6,000 | Remarkable for its high-velocity space motion |
| Sigma 1694 Camelopardalis | 4.51 | Varied | Symbolizes the head of the giraffe figure |
As elusive as its namesake animal, Camelopardalis does not boast the resplendent distinction of more storied star patterns. Still, its narrative—one of recent origin yet laden with the intrigue of pioneering spirit—is an essential piece of the skywatcher’s lexicon. Its constellation history reveals humanity’s insatiable curiosity and the continuous expansion of our celestial cartography.
Camelopardalis Constellation Information: A Treasure Trove for Astronomy Enthusiasts
For those entranced by the mysteries of the night sky, the Camelopardalis constellation harbors a wealth of knowledge and celestial wonders. Sprawling across the firmament, this constellation offers a striking canvas for deep sky exploration. As an astronomy enthusiast, your journey through the Camelopardalis constellation’s expansive domain unveils its intriguing history and the cosmic ballet of its stars and deep sky objects. This northern circumpolar constellation, visible mostly from the Northern Hemisphere, stands out with its unique Camelopardalis star pattern and its enigmatic presence due to the absence of bright stars, marking the sky with a subtlety that challenges and delights stargazers.
Bridging the Knowledge Gap: Key Constellation Facts
Understanding the Camelopardalis constellation begins with grasping its size and position in the night sky. Its vast expanse and location near the North celestial pole mean it never sets below the horizon for observers in the Northern Hemisphere, offering a constant presence in the sky. Despite its lower profile in terms of stellar brightness, the constellation is an essential feature of our cosmic landscape and provides a historical reference to the era of Renaissance astronomy. The Camelopardalis star cluster, while less pronounced, plays a pivotal role in unveiling the expansion of the universe as understood by astronomers of the past.
Camelopardalis Constellation Discoveries and Modern Observations
In your quest for celestial discovery, the Camelopardalis constellation facts enrich your understanding of the cosmic fields. Modern technological advances, such as star charts and stargazing apps, have made it easier to locate and enjoy this constellation’s hidden gems. With its rich tapestry of galaxies and nebulae, Camelopardalis offers a view into the vibrant planetary nebulae and the restless stir of dwarf galaxies harboring stellar nurseries. As you delve into the Camelopardalis constellation history, you surely gaze upon the same night sky that once incited wonder in the hearts of Renaissance explorers, now equipped with the treasure of knowledge that reveals the storytelling of the stars.
FAQ
What is the origin of the name Camelopardalis?
The name Camelopardalis is Latin for “giraffe,” adapted from the Greek words ‘kamēlos’ (camel) and ‘pardalis’ (leopard), referring to the giraffe’s long neck and spotted body. This constellation was created by Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius and first appeared on a star map illustrated by Jakob Bartsch in 1624.
What are some historical discoveries associated with the Camelopardalis constellation?
Camelopardalis is known for the asterism Kemble’s Cascade, the star cluster NGC 1502, and deep sky objects such as the Oyster Nebula (NGC 1501), spiral galaxy NGC 2403, and the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 1569. Its stars include Beta Camelopardalis, the brightest, and it’s known for the October Camelopardalids meteor shower.
What is the Camelopardalis star pattern?
The Camelopardalis star pattern forms a constellation resembling a giraffe, located in the northern sky. It is recognized by its lack of bright stars and hosts a variety of binary and variable stars, as well as deep sky objects. Star patterns like Kemble’s Cascade make it significant, despite the moderate brightness of its stars.
How can I find Camelopardalis in the night sky?
Camelopardalis can be located using a constellation map provided by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) or publications such as Sky & Telescope magazine. It is a large constellation near the northern celestial pole, best observed from the Northern Hemisphere using azimuth and altitude coordinates.
What are some notable features of the Camelopardalis constellation?
Notable features within Camelopardalis include Kemble’s Cascade, a noticeable asterism; the open star cluster NGC 1502; planetary nebulae like the Oyster Nebula (NGC 1501); and several galaxies. This constellation also hosts occasional meteor showers and contains three stars with known planetary systems.
Who is associated with the discoveries within Camelopardalis?
The constellation Camelopardalis was delineated by Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius and later illustrated by Jakob Bartsch. However, many modern discoveries, such as galaxies and nebulae within its boundaries, have been made and documented by various astronomers over the centuries.
What deep sky objects are located in the Camelopardalis constellation?
Deep sky objects in the Camelopardalis constellation include the spiral galaxy NGC 2403, the intermediate spiral galaxy IC 342, the Oyster Nebula (NGC 1501), and the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 1569 with its super star clusters. These objects are significant not only for their distance and size but also for the insights they provide into star formation and galactic structures.
What does the Camelopardalis constellation represent?
Camelopardalis represents the giraffe and is one of the few constellations without ancient mythological associations. It was established during the period of global exploration and named for the exotic creatures that Europeans encountered, symbolizing the mystery of uncharted territories.
What are some bright stars in the Camelopardalis constellation?
While Camelopardalis lacks very bright stars, it is home to Beta Camelopardalis, the brightest star of the constellation, which is a binary system with a G-type supergiant. Other significant stars include CS Camelopardalis, a bright variable star, and Sigma 1694 Camelopardalis, among others.
Are there any resources available for those interested in learning more about the Camelopardalis constellation?
Yes, there are many resources available for those looking to learn more about the Camelopardalis constellation, including star charts, astronomy apps, and scientific publications. Additionally, the International Astronomical Union and Sky & Telescope magazine provide detailed constellation maps for enthusiasts.