| Genitive | Arietis |
| Abbreviation | Ari |
| Pronunciation | (ˈɛəriːz) |
| Main Stars | 4, 9 |
| Brightest Star | Hamal (α Ari) (2.01m) |
| Right Ascension | 1 hour to 3 hours |
| Declination | 31 deg to -10 deg |
| Sq. Deg. Area | 441 |
| Crosses Meridian | 9PM, Dec |
| Visible Lat. Range | +90, -60 deg (°) |
| Best Viewing Season | Autumn (Northern Hemisphere) |
When you gaze up at the night sky, the Aries constellation beckons with its storied stars, a cosmic tapestry woven through time. This group of celestial wonders, identified by the striking Aries astrological symbol ♈, has been guiding humans since antiquity. Known as the ram, its mythological and astrological significance is as vibrant as its stellar composition. Whether you’re an astrology enthusiast attracted by the Aries star sign or an amateur astronomer drawn to its celestial features, Aries offers a fascinating slice of the heavens to explore.
Bearing the tales of the Golden Fleece and marking a prominent position in the Northern Hemisphere, this constellation is dense with history and brilliance. You’ll discover bright stars like Hamal and Sheratan, and deep sky spectacles such as galaxy NGC 772. As a crucial element of the zodiac, the Aries zodiac sign holds a special place in the hearts of those who look to the stars for guidance.
Key Takeaways
- Discover the rich mythology of the Aries constellation, dating back to ancient civilizations.
- Explore the connection between the Aries astrological symbol and its representation of the ram.
- Uncover the significance of the Aries star sign in astrological traditions and horoscopes.
- Learn how to locate the Aries zodiac sign within the tapestry of the Northern Hemisphere’s night sky.
- Gain insights into the bright stars and deep sky objects that define the Aries constellation.
Exploring the Rich History of Aries Constellation
The tapestry of the night sky is embroidered with stories and symbols that have travelled through millennia. Few stories are as enduring as those entwined with the Aries constellation history. As you delve into the ancient world, you’re introduced to Aries’ timeless narrative, from its humble Babylonian beginnings to its significant astrological influence that echoes to this day.
Babylonian Beginnings and Greek Mythology Connections
Once perceived by the Babylonians as a figure of an agrarian worker, the identity of the Aries constellation evolved to host the star Alpha Arietis or Hamal, at the heart of the vernal equinox. As civilizations rose and fell, the image of the Aries ram became rooted in the heavens above and in the rich narratives of Aries Greek mythology. These narratives speak of heroism and adventure – symbolized by the golden ram that delivered Phrixus from peril – and paint a picture of Aries as not just a cluster of stars, but as an emblem of rescue and high sacrifice, immortalized in the tale of Jason and the Argonauts seeking the Golden Fleece.
Astrological Significance Through the Ages
Dating back to antiquity, the Aries astrological symbol has been recognized as a marker of significant celestial events. The vernal equinox, that point in the sky where the sun crosses the celestial equator, was historically nestled within this constellation, making Aries an important signpost in the sky for various cultures. Egyptians saw this moment as a reflection of Amon-Ra, a personification of creativity and rebirth. As you navigate through the annals of history, you’ll find Aries’ impact spread far and wide, its ram’s horns a universal symbol that transcends time and geographic boundaries.
Aries: A Symbol of Rebirth and the Vernal Equinox
In essence, the Aries zodiac sign and the Astrological constellation Aries have served as harbingers of spring throughout the ages, heralding the rejuvenation of the land. The ancients referred to this time as an ‘Indicator of the Reborn Sun,’ a period that carried immense importance. Despite the astronomical shift of the vernal equinox into Pisces over centuries due to precession, the symbolic power of Aries remains unshaken. Your understanding of this constellation is layered with its significance as a symbol of resurrection and new beginnings – essential themes that resonate with every observer gazing upon these stars as the Earth’s cycle continues its eternal round.
Stargazing Aries: Locating the Ram in the Night Sky
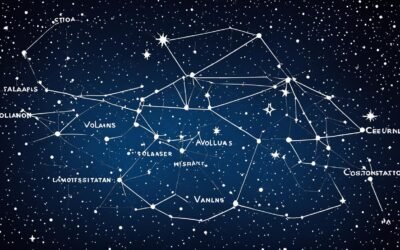
If you’ve ever gazed up at the night sky, intrigued by the tales of constellations that adorn our celestial sphere, locating the Aries constellation can be a thrilling experience. Aries, represented by the powerful symbol of a ram, holds significant intrigue for both astronomers and astrologers alike. When you’re seeking to find this zodiac constellation, understanding the Aries constellation map becomes essential.
The key to spotting Aries is knowing when and where to look. This constellation is prominently situated in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere, making it visible at latitudes between +90° and -60°. To the uninitiated, the night sky might seem like a maze of twinkling lights, but with a basic understanding of the Aries star sign’s neighbors, you’ll be able to navigate the stars like an experienced stargazer.

Aries shares borders with several constellations: Cetus, Perseus, Pisces, Taurus, and Triangulum. Each of these neighboring constellations serves as a landmark that can guide you to Aries. The guidance of an Aries constellation map, such as those detailed by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and Sky & Telescope magazine, can greatly simplify your quest in locating Aries constellation.
| Constellation | Direction from Aries | Notable Star or Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Cetus | Southwest | Menkar and Mira |
| Taurus | East | Aldebaran and the Pleiades cluster |
| Pisces | West | Van Maanen’s Star |
| Perseus | North | Algol (the Demon Star) |
| Triangulum | North | Triangulum Galaxy |
One of the best times to spot Aries is during the late autumn months, particularly if you’re in the Northern Hemisphere. Gazing towards the eastern sky, you should catch sight of Aries as it begins its ascent shortly after sunset. By using both the map and the celestial markers provided by neighboring constellations, you’ll confidently locate the Aries constellation, unveiling its storied patterns woven into the tapestry of our universe.
Constellation Aries: An Astronomical Overview
When you look up at the night sky, Aries constellation beckons as a testament to its ancient roots and celestial significance. This astronomical marvel offers a rich tapestry of Aries constellation facts that blend mythological charm with the marvels of the cosmos. Occupying a specific Aries constellation location in the celestial sphere, Aries has intrigued stargazers and astronomers alike. It is not just another cluster of stars; Aries tells a story that’s weaved into the fabric of the night sky.
As you glance through a telescope, you will find Aries covering an area of 441 square degrees. This expanse makes it the 39th largest constellation out of the 88 recognized by modern astronomers. Within its boundaries, Aries is home to celestial bodies and stellar phenomena that make it an area worth exploring:
- Notable Stars: Aries houses a family of stars that have their unique tales and cosmic dances. These include not just radiant suns like Hamal, but also planets that orbit them, adding to the celestial drama.
- Meteor Showers: The May Arietids, an annual meteor shower, grace the sky with their fleeting presence, creating a spectacle for those lucky enough to witness their journey across our planet’s atmosphere.
- Stellar Phenomena: The constellation is a treasure chest of interesting stellar events, even though it contains no Messier objects, which are typically used as milestones by astronomers.
Whether you’re an avid sky watcher or a curious newcomer, the Aries constellation is a portal to our universe’s past and a beacon for astrophysical education and enjoyment. So next time you gaze upwards, remember that the history, the location, and the facts of Aries are ready to enrich your experience with the grandeur of the cosmos.
Unveiling the Stars of Aries: From Hamal to Sheratan
The Aries constellation, a symbol of the celestial ram, houses an imposing assembly of stars that have guided humanities’ gaze upwards for centuries. As you explore the night sky, the stories of these stars unfold, beginning with the venerated Hamal star, leading through to the dynamic Sheratan, and concluding with the intriguing Mesarthim star system. These luminous beacons are not just points of light but celestial markers of history, mythology, and the marvel of cosmic evolution.
Discover the protagonists of the Aries constellation that have captivated astronomers and stargazers alike.
Hamal: The Brightest Star in Aries and Its Historical Role
Known as Alpha Arietis, Hamal bears the title of the brightest star in Aries. This luminous giant, an orange K-type star, displays a brilliance that varies slightly due to stellar pulsations. Stationed roughly 66 light-years from our planet, Hamal has been a celestial point of reference since antiquity, marking the location of the vernal equinox in a bygone era.
The Spectroscopic Wonders of Sheratan
Encompassing the title of Beta Arietis, Sheratan serves as an astronomical marvel within the Aries constellation stars, operating as part of a spectroscopic binary system. This binary star is a hotbed of astrophysical activity, its interactions revealing the dynamics of stellar relationships. Positioned at a comfortable stargazing distance of 59.6 light-years away, Sheratan shines with a magnitude that renders it a guidepost in the celestial ram’s formation.
Mesarthim and Other Notable Stellar Highlights
Another gem within the Aries constellation is Mesarthim, or Gamma Arietis, a triple star system that forms an integral part of this stellar family. But the treasures of Aries do not conclude with Mesarthim. Aries notable stars such as Botein, Bharani, and Epsilon Arietis share the stage, each contributing to the deep narrative written across the canvas of the night.
Explore beyond the twinkling facade and you’ll encounter the Aries constellation deep sky objects that offer a journey through space and time:

| Star Name | Designation | Type | Light-Years from Earth | Apparent Magnitude | Constellation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hamal | Alpha Arietis | K-type Orange Giant | 66 | 1.98 – 2.04 | Aries |
| Sheratan | Beta Arietis | Spectroscopic Binary | 59.6 | 2.64 | Aries |
| Mesarthim | Gamma Arietis | Triple Star System | Varies | 3.86 (combined) | Aries |
Your celestial tour of the Aries stars reveals a cosmic tableau rich in history and beauty. As you gaze upon these luminaries, you become part of an ancient human tradition, finding your own connection to the vast expanse of the universe.
Deep Sky Wonders within the Aries Constellation
As you shift your gaze towards the Aries constellation, the cosmos unveils its more profound mysteries, presenting deep sky objects that capture the imagination and invite exploration. Within this ancient celestial ram lies a treasure trove of galactic phenomena, from the grandeur of spiral arms to the chaotic beauty of irregular galaxies. Whether you’re an amateur astronomer or a seasoned stargazer, the deep sky objects within Aries offer a remarkable journey through the wonders of the universe.
The Intriguing Spiral Galaxy NGC 772
One such marvel is NGC 772, an unbarred spiral galaxy that resides in the Aries constellation. This striking spiral galaxy, situated approximately 130 million light-years away from our vantage point on Earth, offers a spectacular display for those with telescopic equipment. NGC 772’s elongated and warped arms, peculiarly stretched by gravitational interactions with its companion galaxy, NGC 770, give us insight into the forces at play in the cosmos. This celestial interaction is an exquisite example of the dynamism and ongoing evolution observable within Aries’ deep sky objects.
Discovering Aries’ Dwarf Irregular Galaxy NGC 1156
The allure of Aries’ night sky doesn’t end with spirals. The dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 1156 presents itself as a must-see spectacle for astrophiles. Its form, reminiscent of an ethereal cherry blossom against the cosmic backdrop, is a vibrant testament to the complex life cycles of galaxies. Illuminated by brilliant areas of star formation and swirling gases, NGC 1156 tells a tale of a turbulent history, with regions moving in contrary rotations—an indication of possible gravitational influences from its neighbors. This galaxy, unique among the Aries constellation exploration finds, broadens our understanding of galactic diversity and the processes shaping the universe’s structure.
FAQ
What is the Aries constellation?
The Aries constellation is a collection of stars which is symbolized by a ram, representing the story of the Golden Fleece. It is one of the 88 modern constellations and part of the 12 astrological signs in the Zodiac, known for bright stars such as Hamal and Sheratan.
How is the Aries astrological symbol depicted?
The Aries astrological symbol is depicted as ♈, which resembles a ram’s horns, reflecting the ram symbol of the constellation.
What is the historical significance of the Aries constellation?
Historically, the Aries constellation was significant for marking the location of the vernal equinox, and it has been associated with various mythologies and astrological systems. Its brightest star, Hamal, was once used by ancient cultures to mark the vernal equinox.
What is the connection between Aries and Greek mythology?
In Greek mythology, the Aries constellation is associated with the story of a golden ram that saved Phrixus by carrying him to safety, ultimately leading to the tale of the Golden Fleece and Jason and the Argonauts. This established Aries as a symbol of rescue and sacrifice within Greek mythology.
How does the Aries zodiac sign relate to the Aries constellation?
The Aries zodiac sign is directly associated with the Aries constellation. Individuals born between March 21 and April 19 are considered to be born under the Aries star sign, with personalities believed to be influenced by the traits of the constellation and its symbols.
Where is the Aries constellation located?
The Aries constellation is located in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere and can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -60°. It is bordered by the constellations Cetus, Perseus, Pisces, Taurus, and Triangulum.
Who named the Aries constellation, and when?
The Aries constellation was one of the original 48 constellations listed by the astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century and continues to be one of the modern 88 recognized constellations. The name ‘Aries’ is Latin for ‘the ram.’
What are the main stars in the Aries constellation?
The main stars in the Aries constellation include Hamal (Alpha Arietis), Sheratan (Beta Arietis), and Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis), along with other notable stars such as Botein, Bharani, and Epsilon Arietis.
Are there any special deep sky objects in Aries?
Yes, deep sky objects in Aries include the unbarred spiral galaxy NGC 772 and the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 1156. These intriguing celestial bodies can be observed with amateur telescopes and offer a glimpse into the dynamics of the universe.
What significance does Aries hold in astrology?
In astrology, those born under the Aries zodiac sign are said to exhibit traits such as leadership, confidence, and enthusiasm. Aries’s position at the start of the zodiac symbolizes beginnings and pioneering spirit. It holds astrological significance for representing the initiation of the zodiac wheel and the rebirth of spring.