| Genitive | Arae |
| Abbreviation | Ara |
| Pronunciation | (ˈɛərə) |
| Main Stars | 8 |
| Brightest Star | β Ara (2.84m) |
| Right Ascension | 16 hours to 18 hours |
| Declination | -45 deg to -67 deg |
| Sq. Deg. Area | 237 |
| Crosses Meridian | 9PM, Jul |
| Visible Lat. Range | +25, -90 deg (°) |
| Best Viewing Season | Winter (Southern Hemisphere) |
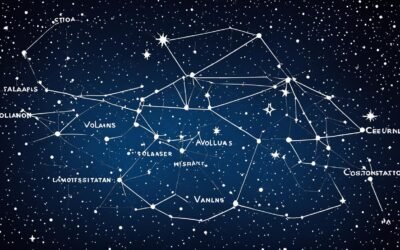
Characteristics of Ara
Ara, known as “the Altar” in Latin, is a constellation nestled in the southern sky. It boasts a distinctive placement between Scorpius, Telescopium, Triangulum Australe, and Norma. This constellation, which spans 237 square degrees making it the 63rd largest in the night sky, is visible predominantly to observers located south of 22°N latitude. Ara’s brightest star, Beta Arae, shines with an apparent magnitude of 2.85, slightly outshining Alpha Arae. The constellation contains seven star systems known to host planets, with the Milky Way gracing its northwestern part. Westerlund 1, a super star cluster within Ara, hosts one of the largest known stars, Westerlund 1-26.
Discovery and History
The ancient Greeks recognized Ara as the altar where gods formed alliances before their battle with the Titans. Described by Ptolemy in the 2nd century, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ara’s depiction has varied throughout history, from classical altars to ones surrounded by demons in early prints. In different cultures, such as Chinese astronomy, the stars of Ara were associated with symbols like the tortoise and the pestle.
Visibility of Ara
Ara is primarily visible in the Southern Hemisphere, from latitudes between +25° and −90°. It reaches its highest point in the night sky at 21:00 during July. While it is a southern constellation, its visibility extends to the Northern Hemisphere up to a latitude of 25°N. Therefore, Ara is visible from both hemispheres, but its full glory is best appreciated in the southern skies.
Best Time to Observe Ara
The constellation Ara is best observed in July when it is most prominent in the sky. Observers in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres can catch a glimpse of Ara, although it is more prominently visible from the Southern Hemisphere. It does not remain visible all year; its visibility peaks during the winter months in the Southern Hemisphere, aligning with the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere.
Identification and Major Stars
Identifying Ara in the night sky involves looking for its brightest star, Beta Arae, an orange supergiant. Right beside it, you will find Alpha Arae, a blue-white star that stands as the constellation’s second brightest member. The constellation sprawls across right ascension coordinates from 16h 34m to 18h 10m and declination coordinates from -45.4859734° to -67.6905823°. This celestial altar is composed of eight main stars, with its area totaling 237 square degrees.
Symbolism and Mythology
Ara symbolizes an altar, with its mythological roots tracing back to ancient Greece where it was associated with the altar used by the Olympian gods. Its origins also tie to Babylonian culture, where it represented the altar honoring the Tower of Babel. In Greek mythology, Ara was linked to the altar where Chiron, the centaur, made sacrifices, symbolizing unity among the gods.
Deep Sky Objects
Ara is home to several notable deep sky objects, including:
- NGC 6193: A large open cluster containing 27 stars, illuminating the emission nebula NGC 6188.
- NGC 6397: One of the nearest globular clusters to Earth, containing about 400,000 stars.
- The Stingray Nebula: The youngest known planetary nebula, located approximately 18,000 light years from Earth.
- NGC 6362: A globular cluster estimated to be 13.57 billion years old.
Neighboring Star Clusters
Ara’s celestial neighborhood includes several star clusters, both globular and open, such as NGC 6352, a relatively loose globular cluster, and Westerlund 1, noted for containing the red supergiant Westerlund 1-26.
This constellation, steeped in mythology and adorned with celestial marvels, offers a fascinating glimpse into the cosmos for stargazers and astronomers alike.